Your Complete Guide to Understanding Feasibility Studies: 7 Types, Financial Indicators, and How to Read Them Like a Pro 2025

A comprehensive detailed guide about economic feasibility studies: Learn about the 7 types (marketing, technical, financial, legal), how to read NPV, IRR, and ROI indicators, and requirements from Saudi Development Bank, Monsha'at, and Industrial Development Fund for obtaining financing.
Introduction: Why Do 60% of New Projects Fail?
The statistics are shocking: more than 60% of small and medium enterprises fail within the first five years. The main reason? It's not lack of funding as many believe, but rather the absence of proper planning and not conducting a real feasibility study before starting.
A feasibility study is not just a "paper" you submit to the bank for a loan. It's a roadmap that reveals the naked truth: Will your idea actually succeed or will you burn your money and time? Is the market ready for your product? Will you make profits worth the risk?
In this comprehensive guide, we'll take you on a deep journey to understand everything you need to know about feasibility studies: their seven types, the financial indicators you must understand, how to read a study like a professional investor, and which Saudi entities require them and how to meet their requirements.
First: What Exactly is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a comprehensive systematic analytical process aimed at evaluating the viability and success potential of a specific project from all aspects: economic, technical, financial, legal, social, and environmental.
In simpler words: A feasibility study answers one fundamental question: "Is this project worth investing my time, money, and effort in?"
The Difference Between a Feasibility Study and a Business Plan
Many confuse these two concepts, but they are completely different:
A feasibility study is conducted before making the decision to start a project. Its goal is to answer the question: "Should we start or not?" It focuses on analysis and objective evaluation. It may conclude with a recommendation to reject the project if it's not viable.
A business plan is prepared after making the decision to start a project. Its goal is to answer the question: "How do we execute?" It focuses on detailed planning for execution. It assumes the project will be implemented and sets out the execution steps.
When Do You Need a Feasibility Study?
You need a feasibility study in several key situations: When considering launching a new project. When applying for financing from a bank or investment fund. When entering into partnership with local or foreign investors. When expanding an existing project or adding a new production line. When acquiring or merging with another company. When requesting a license from certain government entities.

Second: The Seven Types of Feasibility Studies
A comprehensive feasibility study is not one study, but a set of integrated studies, each focusing on a specific aspect of the project. Understanding these types is essential because each type answers different questions.
1. Market Feasibility Study
This is the starting point and foundation upon which all other studies are built. If there's no market for your product, there's no point in any other study.
What does market feasibility include? Analysis of current and expected market size. Study of demand for the product or service. Analysis of competitors and their strengths and weaknesses. Identification of target segment and its characteristics. Study of consumer behavior and preferences. Identification of the marketing gap (difference between supply and demand). Pricing strategy development. Identification of appropriate distribution channels. Estimation of expected market share.
Why is it the most important? Because its results determine whether you'll continue with the remaining studies or stop. If the market study shows the market is saturated or demand is weak, it's better to stop here and save the costs of other studies.
2. Technical Feasibility Study
After confirming market existence, the technical study comes to answer the question: "Can we technically produce this product or provide this service?"
What does technical feasibility include? Determining the optimal project location and its justifications. Determining project size and production capacity. Selecting appropriate technology and production method. Identifying required equipment and machines and their specifications. Identifying raw materials and their sources. Identifying workforce requirements (number, qualifications, specializations). Internal layout of the factory or facility. Determining the implementation schedule. Estimating the project's useful life.
Its importance: The technical study is the foundation upon which the financial study is built, as it determines all cost elements.
3. Financial Feasibility Study
This is the study that investors and banks focus on more than any other. It answers the most important question: "Will the project achieve profits worth the risk?"
What does financial feasibility include? Determining investment costs (capital required to start). Determining operational costs (ongoing expenses). Estimating expected revenues. Preparing projected income statement. Preparing cash flow statement. Calculating break-even point. Calculating financial indicators (NPV, IRR, ROI, payback period). Identifying funding sources and structure. Preparing loan repayment schedule.
We will cover financial indicators in detail in a later section.
4. Economic Feasibility Study
This differs from the financial study in that it looks at the project from a broader perspective: its impact on the national economy, not just on the project owner.
What does it include? Cost-benefit analysis from a macroeconomic perspective. Measuring the impact on gross domestic product. Evaluating contribution to reducing imports or increasing exports. Measuring the impact on the balance of payments. Evaluating efficiency in using national resources.
When is it important? This study is essential for major projects seeking government support, as the government wants to ensure the project will benefit the national economy, not just its owner.
5. Legal Feasibility Study
Ensures the project complies with all applicable laws and regulations.
What does it include? Required licenses and permits. Appropriate legal form for the project (limited liability company, sole proprietorship, etc.). Tax and zakat obligations. Labor and social insurance laws. Intellectual property rights and patents. Necessary contracts and agreements. Saudization requirements and localization ratios.
6. Environmental Feasibility Study
This study has become mandatory for many projects, especially industrial ones.
What does it include? Environmental impact assessment of the project. Expected emissions and pollutants. Waste treatment plans. Natural resource consumption (water, energy). Compliance with Saudi and international environmental standards. Plans to mitigate negative effects.
7. Social Feasibility Study
Measures the project's impact on the local community.
What does it include? Number of job opportunities the project will provide. Impact on local community. Contribution to regional development. Compatibility with social values and customs. Corporate social responsibility programs.
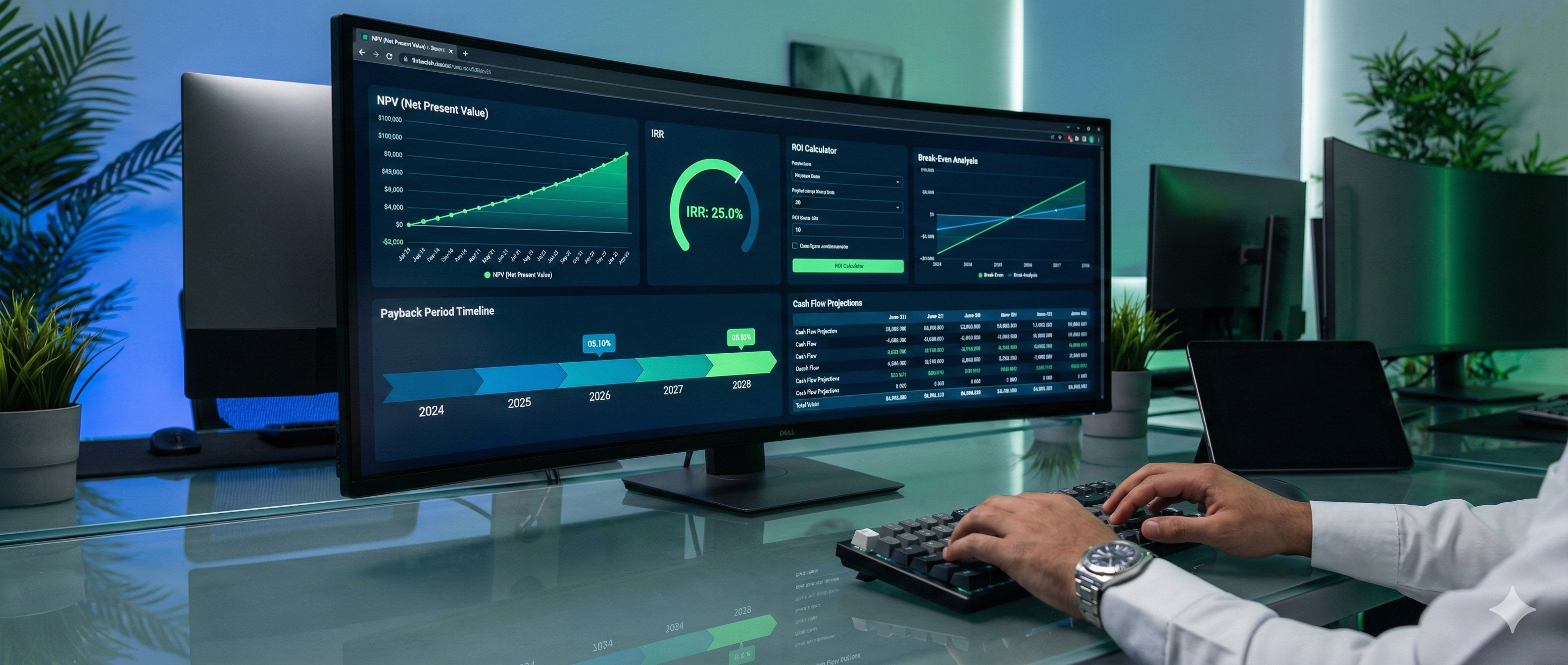
Third: The Five Financial Indicators You Must Understand
These indicators are the "language" of investors and banks. If you don't understand them, you won't be able to read a feasibility study correctly, and you won't be able to convince any funder of your project.
1. Net Present Value (NPV)
What is it? Net Present Value is the difference between the present value of all expected future cash flows from the project and the present value of the initial investment.
In simpler words: It's the "real profit" value from the project after accounting for the fact that money you'll receive in the future is worth less than money you have today.
How to read it? If NPV is positive (greater than zero): The project is profitable and worth investing in. If NPV is negative (less than zero): The project is losing and should be avoided. If NPV equals zero: The project achieves exactly the required return, no additional profit.
Practical example: If your project's NPV equals 500,000 SAR, this means the project will add half a million riyals to your wealth above the expected return.
2. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
What is it? It's the discount rate that makes the Net Present Value (NPV) equal zero. In other words, it's the "actual rate of return" that the project achieves.
How to read it? Compare IRR to the cost of capital or alternative return. If IRR is higher than financing cost: The project is viable. If IRR is lower than financing cost: The project is not viable.
Practical example: If your project's IRR is 25% and the bank loan cost is 8%, the project is excellent because it achieves a return much higher than the financing cost. But if IRR is only 6%, it's better to put your money in a bank deposit instead of risking a project.
3. Payback Period
What is it? It's the time required to recover the invested capital from the project's cash flows.
How to read it? The shorter the payback period, the better the project in terms of risk. Usually, investors prefer projects that recover their capital within 3-5 years.
How is it calculated? For equal cash flows: Payback Period = Initial Investment ÷ Annual Cash Flow. Example: An investment of one million riyals with annual flow of 250,000 riyals = 4 years for recovery.
For unequal cash flows: Calculated by accumulating flows year by year until they equal the initial investment.
Important warning: Payback period alone is not sufficient for decision-making because it doesn't consider the time value of money or profits after the payback period.
4. Return on Investment (ROI)
What is it? It's the ratio of profit to invested capital, expressed as a percentage.
How is it calculated? ROI = (Net Profit ÷ Investment Cost) × 100
Example: If you invested one million riyals and achieved a net profit of 200,000 riyals, then ROI = 20%.
How to read it? The higher the ROI, the better the project. Compare it to alternative returns (bank deposits, stocks, real estate) to know if it's worth the risk.
5. Break-even Point
What is it? It's the point where revenues equal costs, meaning no profit and no loss.
Why is it important? It tells you the minimum sales that must be achieved to cover costs. Any sales above break-even translate into profits.
How is it calculated? Break-even in units = Fixed Costs ÷ (Selling Price - Variable Cost per Unit)
Example: If fixed costs are one million riyals, unit selling price is 100 riyals, and variable cost is 60 riyals, then break-even = 1,000,000 ÷ 40 = 25,000 units. This means you must sell at least 25,000 units to cover costs.
Indicator Comparison Table
For easier understanding, here's a quick summary:
Net Present Value NPV answers the question: How much will the project add to my wealth? The rule is the higher the better, with the minimum acceptable being greater than zero.
Internal Rate of Return IRR answers the question: What is the actual rate of return? The rule is it must be higher than financing cost.
Payback Period answers the question: When will I recover my money? The rule is the shorter the better, preferably less than 5 years.
Return on Investment ROI answers the question: What is the profit percentage to investment? The rule is the higher the better.
Break-even Point answers the question: How much must I sell to cover costs? The rule is it must be realistically achievable.

Fourth: How to Read a Feasibility Study Like a Professional Investor
Whether you're the project owner or an investor studying an opportunity, here are the methodical steps to read and evaluate a feasibility study:
Step 1: Start with the Executive Summary
The executive summary gives you a quick picture of the project. Look for: Clear project idea. Required investment amount. Expected returns. Key risks. Final recommendation.
Step 2: Verify the Marketing Gap
Ask yourself: Is there really unsatisfied demand in the market? What is the size of this gap? Is the data used recent and reliable? Is the competitor analysis realistic or overly optimistic?
Step 3: Review the Assumptions
Every feasibility study is built on assumptions. Ask: Are the assumptions realistic? What are the sources of the numbers used? Were different scenarios tested (optimistic, pessimistic, realistic)?
Step 4: Study the Financial Indicators
Don't settle for looking at one number. Compare all indicators. Ensure NPV is positive and IRR is higher than financing cost. Verify payback period is reasonable. Ensure break-even is realistically achievable.
Step 5: Read the Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis tells you: What happens if sales drop 10% or 20%? What if costs increase? What if project implementation is delayed? This analysis reveals how "solid" the project is against changes.
Step 6: Review the Risk Plan
Every project has risks. A good study clearly identifies them and sets plans to deal with them. Beware of studies that show the project as "perfect" without any risks!
Warning Signs in a Feasibility Study
Beware of these signs indicating a weak or unreliable study:
Overly rounded numbers such as all costs being in exact millions. Absence of data sources or use of outdated sources. Very optimistic forecasts without justification. Absence of competitor analysis or underestimating them. No sensitivity analysis. Absence of risk management plan. Ignoring legal and regulatory aspects.
Fifth: Saudi Entities That Require Feasibility Studies
In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, there are several government and financing entities that require submitting an accredited feasibility study to obtain financing or support. Understanding each entity's requirements increases your application's chances of acceptance.
1. Social Development Bank
Who is it? A government bank that aims to support small and emerging projects and economically empower individuals.
Its main programs: "Asl" program for small project financing. "Masarat" program for entrepreneurs. Productive family financing. Financing for people with disabilities and widows.
Feasibility study requirements: Clear identification of project idea. Location study and justifications. Market and competitor analysis. Technical and operational study. Financial projections for 3-5 years. Identification of funding sources. Risk management plan.
Tip: The bank focuses on small and medium projects, so ensure your study shows your ability to repay and employ Saudis.
2. General Authority for Small and Medium Enterprises (Monsha'at)
Who is it? A government authority that supports the SME sector with financing, training, and consulting.
Its programs: Various financing programs. Business acceleration programs. Incubator and accelerator programs.
Feasibility study requirements: Comprehensive business plan. Market and opportunity study. Financial model. Growth and expansion plan. Team and their experience.
3. Saudi Industrial Development Fund (SIDF)
Who is it? A government fund specialized in financing industrial, energy, and mining projects.
Types of financing: Long-term loans for industrial projects. Equipment purchase financing. Working capital financing.
Feasibility study requirements: Detailed industrial market study. Detailed technical engineering study. Production plan and capacity. Industrial cost analysis. Environmental impact study. Long-term financial projections (10 years or more).
Tip: This fund deals with large projects, so it requires more detailed and professional studies. It's advisable to use a specialized consulting firm.
4. Saudi Export-Import Bank
When do you need it? If your project targets export or import.
Requirements: Feasibility study highlighting commercial viability from an international trade perspective. Analysis of target export markets. International marketing plan.
5. Commercial Banks
When do you need them? When requesting a commercial loan for your project.
General requirements: Feasibility study from an accredited entity. Financial statements (for existing projects). Required guarantees. Credit record.
6. Ministry of Investment (MISA)
When do you need it? For foreign investors wishing to invest in Saudi Arabia.
Requirements: Feasibility study showing the project's economic impact. Employment and Saudization plan. Compliance with local regulations.
Accredited Study Criteria
For your study to be accepted by these entities, it must be: Comprehensive covering all aspects (market, technical, financial, legal). Prepared by a licensed and accredited consulting entity. Based on recent and reliable data from the Saudi market. Containing realistic and verifiable projections. Accompanied by detailed analytical tables. Compliant with the target entity's requirements.
Sixth: Common Mistakes in Feasibility Studies
Learn from others' mistakes and avoid these fatal errors:
1. Overestimating Revenues
The most common mistake. Many set overly optimistic sales expectations without realistic basis. Result: Project failure due to not achieving expected sales.
2. Underestimating Costs
Many forget hidden costs such as: Establishment and licensing costs. Working capital. Marketing costs. Unexpected expenses. Maintenance and depreciation costs.
3. Ignoring Competition
Underestimating competitors' strength or ignoring them entirely. The market is rarely empty, and even if it is, competitors will enter once they see your success.
4. Using Outdated Data
Markets change quickly, especially after the COVID pandemic and Vision 2030 transformations. Use recent data not exceeding one year.
5. Absence of Sensitivity Analysis
A study that assumes everything will go according to plan is incomplete. What if sales drop? What if costs increase?
6. Copying Ready-made Studies
Using ready templates or copying similar project studies without modification. Every project is unique with its own circumstances.
7. Ignoring Non-Financial Aspects
Focusing only on numbers and ignoring legal, environmental, and social aspects may lead to costly surprises later.
Seventh: Sensitivity Analysis - Testing Your Project's Robustness
Sensitivity analysis is a powerful tool that measures how your project's profitability is affected by changes in key variables.
Why is it Important?
Because the projections in a feasibility study are just estimates. Reality may differ. Sensitivity analysis tells you: Which variables most affect project profitability? What safety margin do you have? Which scenarios make the project unprofitable?
Key Variables to Test
Sales volume: What if sales drop 10%, 20%, 30%? Selling price: What if you have to lower prices due to competition? Costs: What if raw material or labor costs increase? Implementation period: What if the project is delayed 6 months or a year?
How to Read Sensitivity Analysis Results
If the project remains profitable even with 20% sales decline: Strong and relatively safe project. If the project becomes unprofitable with only 5% sales decline: Fragile and risky project.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does preparing a feasibility study cost in Saudi Arabia?
Cost varies depending on project size and complexity. For small projects, it ranges from 5,000 to 15,000 SAR. For medium projects, from 15,000 to 50,000 SAR. For large and industrial projects, it may reach 100,000 SAR or more.
How long does it take to prepare a feasibility study?
Depends on project size and complexity. Small projects: 2 to 4 weeks. Medium projects: 4 to 8 weeks. Large projects: 2 to 6 months.
Can I prepare the feasibility study myself?
Yes, for small projects you can prepare an initial study yourself. But to obtain financing from official entities, you usually need a study from an accredited entity.
What's the difference between preliminary and detailed feasibility studies?
Preliminary study is a quick and brief study to evaluate the idea generally before investing in a detailed study. Detailed study is a comprehensive and in-depth study prepared after passing the preliminary study.
Does a feasibility study guarantee project success?
No, a feasibility study reduces risks and increases success chances, but doesn't guarantee it. Good execution and effective management are no less important than the study itself.
When should a feasibility study be updated?
If more than a year has passed since its preparation. If market conditions have changed significantly. If relevant laws and regulations have changed. Before applying for additional financing.
What is the most important part of a feasibility study?
The marketing study is most important because it's the foundation. If there's no market, there's no point in the rest of the studies. But the financial study is most important for investors and funders.
Conclusion
A feasibility study is not just a bureaucratic requirement or a paper you submit to the bank. It's a powerful tool that protects you from losing your money and time on a project doomed to fail. It's also a roadmap that increases your chances of success if the project is viable.
Key points to remember: A feasibility study precedes the start decision, not the other way around. There are seven types of studies, each answering different questions. The five financial indicators (NPV, IRR, payback period, ROI, break-even point) are investors' language. Sensitivity analysis reveals the project's robustness against changes. Saudi entities have specific requirements that must be met.
Invest in a good feasibility study before investing in your project. The small cost of the study may save you losses of hundreds of thousands or millions.
Share this guide with everyone thinking of starting a project. Proper knowledge is the first step toward success.
