Complete Servers & IT Certifications Guide 2026: From Beginner to Expert - AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, CompTIA
A comprehensive guide about servers and their types (physical, cloud, VPS, dedicated) and IT career paths. Includes detailed coverage of AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and CompTIA certifications, with a learning plan from scratch, expected salaries up to $150,000 annually, and free learning resources.
Introduction: The World of Servers and Endless IT Opportunities
In the age of digital transformation, servers and cloud computing have become the backbone of everything we use daily. From mobile apps to websites, from online games to banking services, everything runs on servers.
The numbers are amazing: the cloud computing market will exceed $723 billion in 2025, with annual growth exceeding 21%! Over 96% of companies use public cloud services. This means massive demand for specialists in this field.
The good news? You can enter this lucrative field without a university degree! Professional certifications like AWS, Azure, and CompTIA have become the gold standard for employment. Certified cloud specialists earn salaries ranging from $120,000 to $150,000 annually.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll take you on a journey from understanding server basics to obtaining certifications that open doors to the best jobs in the world.
First: What Are Servers?
A server is a powerful computer designed to provide services and resources to other devices over a network. While your personal computer is designed for one user, a server is designed to serve hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously.
What Does a Server Do?
Servers perform multiple tasks depending on their type: hosting websites and web applications, storing and sharing data and files, running databases, managing email, running online games, processing complex calculations, and providing AI and machine learning services.
Basic Server Components
A server consists of the same components as a regular computer but with higher specifications: CPU (usually multiple high-performance processors), RAM (massive, can reach hundreds of gigabytes), Storage (usually fast SSDs with RAID systems for protection), Network Cards (high-speed and multiple), and Power Supply (dual for continuity).
Second: Types of Servers
There are multiple classifications for servers. Let's understand them in detail:
First Classification: By Physical Form
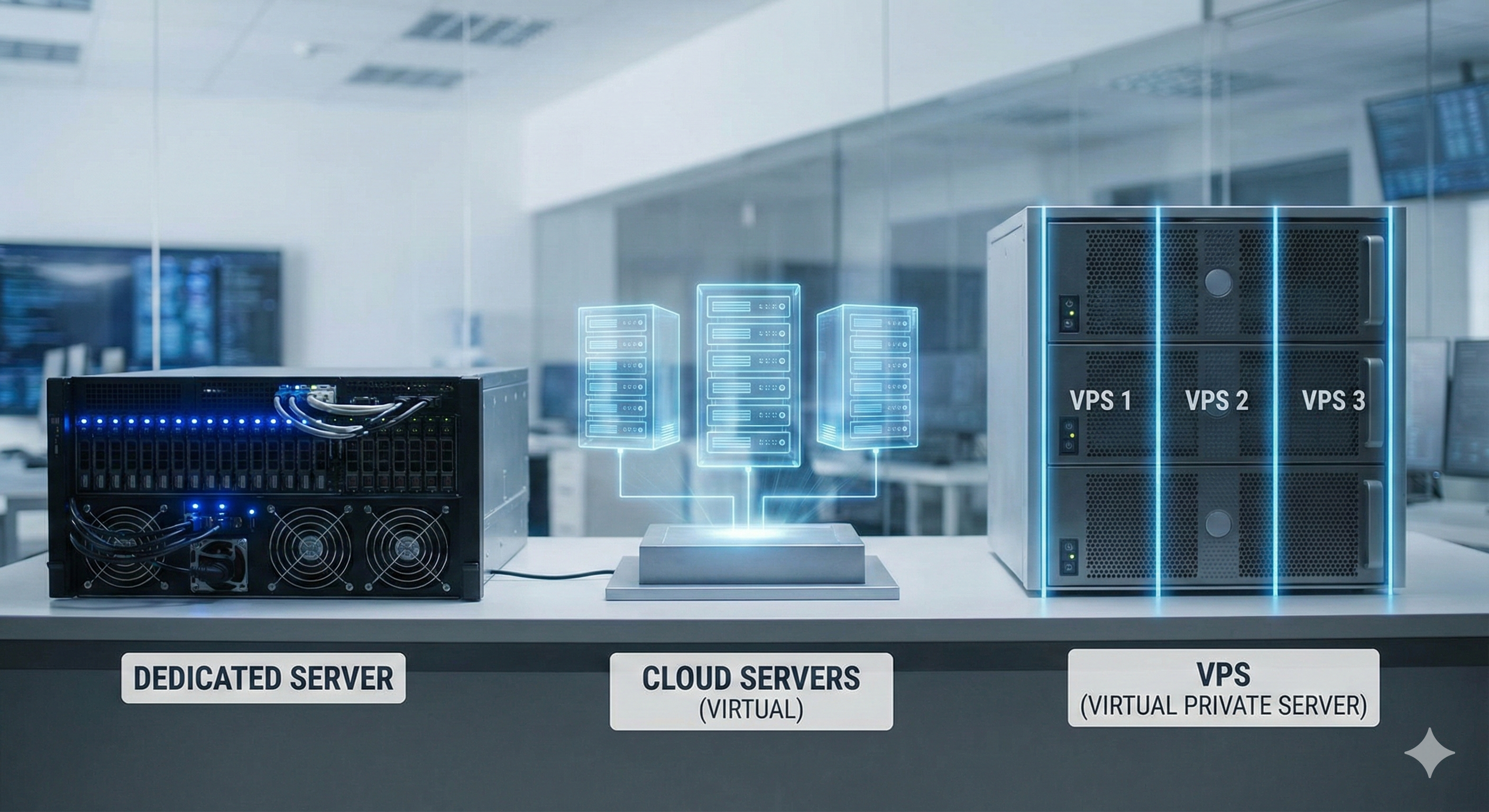
Physical/Dedicated Server
A real, tangible device located in a data center. You have complete control over hardware and software. All resources are dedicated to you alone. Most expensive but highest performance. Suitable for large companies and sensitive applications.
Virtual Server/VPS
A virtual environment on a shared physical server. Software called a Hypervisor divides the physical server into multiple virtual servers. Each VPS has its dedicated resources of RAM and CPU. Cheaper than dedicated server with high flexibility. Suitable for medium projects and growing websites.
Cloud Server
A virtual server running on distributed cloud infrastructure. Resources can be increased or decreased instantly as needed. You only pay for what you use. High flexibility and excellent availability. Provided by companies like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
Second Classification: By Hosting Type
Shared Hosting
Multiple websites share the same server and same resources. Cheapest and suitable for small websites. Limited performance and affected by other websites on the same server. No control over server settings.
VPS Hosting
Dedicated resources for you on a shared server. Complete control over operating system and software. Better performance than shared hosting. Medium price and flexibility in scaling.
Dedicated Hosting
An entire server for you alone. Highest performance and security. Complete control over everything. Most expensive and requires expertise to manage.
Cloud Hosting
Your site runs on a network of servers. If one server stops, work transfers to another automatically. Superior flexibility in scaling. Pay per use.
Third Classification: By Function
Web Server
Hosts websites and responds to HTTP requests. Most famous software: Apache, Nginx, and IIS.
Database Server
Stores and manages data. Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Oracle.
File Server
Stores files and enables sharing across the network.
Mail Server
Manages sending and receiving email.
Application Server
Runs business applications and software.
Game Server
Hosts multiplayer games.
Third: Comparison Between Cloud Service Providers
Three companies dominate the global cloud market:
Amazon Web Services - AWS
The largest globally with 31% market share. Over 200 cloud services. Most mature and documented. Used by Netflix, Airbnb, and NASA. Ideal for startups and cloud-native projects.
Microsoft Azure
Second globally with 24% share. Excellent integration with Microsoft products. 95% of Fortune 500 companies use it. Ideal for companies using Microsoft environment. Strong in Hybrid Cloud solutions.
Google Cloud Platform - GCP
Third globally with 10% share. Strongest in big data and artificial intelligence. BigQuery and Vertex AI are among the best tools. Used by Spotify and Twitter. Ideal for ML projects and data analysis.

Fourth: IT Career Path - Where to Start?
If you're a beginner wanting to enter the IT and servers field, here's the ideal path:
Phase One: Basics (1-3 months)
Before any certification, you must understand the basics: Windows and Linux operating systems, networking basics like IP, DNS, and DHCP, cybersecurity basics, and hardware concepts.
Phase Two: Basic CompTIA Certifications (3-6 months)
CompTIA offers vendor-neutral certifications not tied to any specific company:
CompTIA A+
The ideal starting point. Covers IT basics and technical support. Qualifies you for Help Desk and IT Support jobs. Exam cost around $246. Expected salary: $36,000 - $48,000 annually.
CompTIA Network+
The next step after A+. Covers networking in depth. Qualifies you for Network Administrator jobs. Necessary before Security+.
CompTIA Security+
Most important cybersecurity certification for beginners. Globally recognized especially in government sector. Qualifies you for Security Analyst jobs. Expected salary: $70,000 - $90,000 annually.
Phase Three: Cloud Certifications (6-12 months)
After basics, choose your suitable cloud path:
AWS Path
AWS Cloud Practitioner is a foundational certification to understand AWS costing $100. Then AWS Solutions Architect Associate is the most in-demand in the market costing $150 with expected salary of $120,000 annually. Then AWS Solutions Architect Professional for advanced level.
Azure Path
AZ-900 Azure Fundamentals is a foundational certification with free preparation. Then AZ-104 Azure Administrator. Then AZ-305 Azure Solutions Architect Expert.
Google Cloud Path
Google Cloud Digital Leader is foundational. Then Associate Cloud Engineer. Then Professional Cloud Architect with expected salary of $129,000 annually.

Fifth: AWS Certifications in Detail
AWS is the largest globally and has the most in-demand certifications:
Foundational Level
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
No prior experience needed. Covers basic cloud concepts and main services. Exam duration 90 minutes with 65 questions. Exam cost $100. Ideal as a starting point.
Associate Level
AWS Solutions Architect Associate
Most popular and most in-demand. Requires 6-12 months AWS experience. Covers distributed systems design and security. Exam duration 130 minutes. Exam cost $150. Expected salary: $120,000 - $150,000 annually.
AWS Developer Associate
For developers building applications on AWS. Covers Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB.
AWS SysOps Administrator Associate
For system administrators. Covers deployment, management, and monitoring.
Professional Level
AWS Solutions Architect Professional
For experts. Requires at least two years experience. One of the hardest and highest-paying certifications.
AWS DevOps Engineer Professional
Combines development and operations.
Specialty Certifications
AWS offers specialty certifications in: Machine Learning, Security, Database, Data Analytics, and Networking.
Sixth: Microsoft Azure Certifications in Detail
Azure is very strong in enterprise environments:
Foundational Level
AZ-900 Azure Fundamentals
No technical experience needed. Covers cloud concepts and basic Azure services. Exam cost $99. Microsoft Learn provides free preparation content.
Associate Level
AZ-104 Azure Administrator
For managing Azure resources. Covers identities, networks, and storage. Recommended before AZ-305.
AZ-204 Azure Developer
For developers. Covers building cloud applications.
AZ-500 Azure Security Engineer
For cybersecurity in Azure.
Expert Level
AZ-305 Azure Solutions Architect Expert
For architects. Designing integrated Azure solutions. Requires 1-2 years experience. Expected salary: $130,000 annually.
Seventh: Google Cloud Certifications in Detail
GCP excels in data and artificial intelligence:
Foundational Level
Cloud Digital Leader
For beginners and business people. General understanding of GCP and its benefits.
Associate Level
Associate Cloud Engineer
Deploying and managing applications on GCP. Requires 6 months experience.
Professional Level
Professional Cloud Architect
Designing integrated GCP solutions. Exam cost $200. Expected salary: $129,000 annually.
Professional Data Engineer
For big data specialists. One of the highest-paying certifications. Covers BigQuery and Dataflow.
Professional Machine Learning Engineer
For AI specialists. Covers Vertex AI and TensorFlow.
Eighth: Salary Comparison by Certification
Here are average annual salaries in the United States for 2026:
CompTIA Certifications
CompTIA A+ salary $36,000 to $48,000. CompTIA Network+ salary $50,000 to $70,000. CompTIA Security+ salary $70,000 to $90,000.
AWS Certifications
AWS Cloud Practitioner salary $70,000 to $90,000. AWS Solutions Architect Associate salary $120,000 to $150,000. AWS Solutions Architect Professional salary $150,000 to $180,000.
Azure Certifications
AZ-900 salary $60,000 to $80,000. AZ-104 salary $90,000 to $120,000. AZ-305 salary $130,000 to $160,000.
Google Cloud Certifications
Associate Cloud Engineer salary $100,000 to $120,000. Professional Cloud Architect salary $129,000 to $150,000. Professional Data Engineer salary $130,000 to $155,000.
Advanced Security Certifications
CISSP salary $135,000 to $170,000.
Ninth: Practical Plan to Start from Scratch
Here's a realistic plan to transition from beginner to professional:
Month 1-2: Basics
Learn Linux basics through free YouTube courses. Understand networking basics TCP/IP, DNS, and DHCP. Install VirtualBox and try different operating systems. Create a free account on AWS, Azure, or GCP.
Month 3-4: CompTIA A+ or Cloud Practitioner
If you're a complete beginner, start with CompTIA A+. If you have a technical background, start with AWS Cloud Practitioner or AZ-900. Use Udemy or Coursera for courses.
Month 5-6: Deepening Cloud Knowledge
Choose your path: AWS, Azure, or GCP. Start preparing for intermediate certification. Execute practical projects using the Free Tier.
Month 7-9: Intermediate Certification
Study deeply for Solutions Architect Associate or AZ-104. Execute practical labs. Take practice exams.
Month 10-12: Job Search
Update LinkedIn and add your certifications. Build a portfolio with your projects. Apply for jobs confidently.

Tenth: Free and Paid Learning Resources
Free Resources
AWS Free Tier is a free account for 12 months. Microsoft Learn is Microsoft's free official platform. Google Cloud Skills Boost with free credit for learning. YouTube with channels like TechWorld with Nana and NetworkChuck. freeCodeCamp for learning programming. Linux Academy with some free content.
Recommended Paid Resources
A Cloud Guru is the best for cloud certifications. Udemy where you can search for Stephane Maarek courses for AWS. Coursera with official certificates from Google and AWS. Pluralsight and KodeKloud for advanced technical content. Tutorials Dojo for excellent practice exams.
Tools for Practical Training
AWS CloudFormation for Infrastructure as Code. Terraform for infrastructure across different clouds. Docker and Kubernetes for containers. Ansible for configuration automation.
Eleventh: Tips for Exam Success
Before the Exam
Study the official Exam Guide carefully. Execute practical projects, not just theory. Take practice exams until you score 80% or more. Review official White Papers.
Exam Day
Sleep well the night before. Read each question carefully. Don't spend too much time on one question. Review your answers at the end.
After the Exam
Celebrate your success. Add the certification to LinkedIn immediately. Start preparing for the next certification. Share your experience to help others.
Twelfth: Available Jobs After Certifications
Entry Level
Help Desk Technician with salary $35,000 to $45,000. IT Support Specialist with salary $40,000 to $55,000. Junior System Administrator with salary $50,000 to $65,000.
Mid Level
Cloud Engineer with salary $90,000 to $120,000. DevOps Engineer with salary $100,000 to $140,000. Network Administrator with salary $70,000 to $95,000. Security Analyst with salary $80,000 to $110,000.
Advanced Level
Cloud Solutions Architect with salary $130,000 to $180,000. Site Reliability Engineer with salary $140,000 to $190,000. Security Architect with salary $150,000 to $200,000. CTO/VP of Engineering with salary $200,000 and above.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need a university degree to work in IT?
No, professional certifications and practical experience have become sufficient in many companies. Companies like Google and Apple have removed the university degree requirement.
Which cloud should I choose: AWS, Azure, or GCP?
If you're unsure, start with AWS as it's the largest in the market. If your company uses Microsoft, choose Azure. If you're interested in data and AI, choose GCP.
How long does it take to get a certification?
Foundational certifications: 1-2 months of study. Intermediate: 2-4 months. Advanced: 3-6 months.
Are certifications worth the investment?
Yes, studies show that certification holders earn 20-30% higher salaries than non-certified professionals.
Can I work remotely?
Yes, most IT and cloud jobs can be done remotely. This is one of the biggest advantages of the field.
What's the difference between System Admin and DevOps?
System Admin manages systems and servers. DevOps combines development and operations with focus on automation and CI/CD.
Should I learn Linux or Windows first?
It's preferable to learn both, but Linux is more commonly used in cloud servers.
Conclusion
The servers and cloud computing field is one of the most in-demand and highest-paying fields in technology. With the cloud market growing over 20% annually, opportunities are endless.
The beautiful thing about this field is that you don't need a university degree to start. Professional certifications like AWS, Azure, and CompTIA have become the gold standard for employment. And you can learn independently through available free resources.
Start today! Create a free account on one of the cloud platforms. Start with a foundational course. Execute practical projects. Get your first certification. Within a year, you could be in a job with a salary exceeding $100,000 annually.
The future is cloud, and you can be part of it!
