Complete Excavation Guide: Soil Types, Equipment, Problems, Solutions, and Real Costs 2025

Detailed guide on land excavation before construction in Saudi Arabia. Learn about six soil types, soil testing procedures and costs, appropriate excavation equipment for each soil, and how to handle groundwater and rocky terrain. Real prices and market information.
Introduction: Why Excavation Is the Most Critical Construction Phase
Before thinking about concrete, steel, and finishing, there's a phase that determines your entire building's fate: the excavation phase. Many people rush through this stage or ignore its importance, only to pay the price later with wall cracks, foundation settlement, or endless moisture problems.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll cover everything you need to know about excavation: soil types in Saudi Arabia, how to test soil and its cost, appropriate equipment for each type, and most importantly, how to handle problems you may encounter during excavation such as groundwater or rocks.
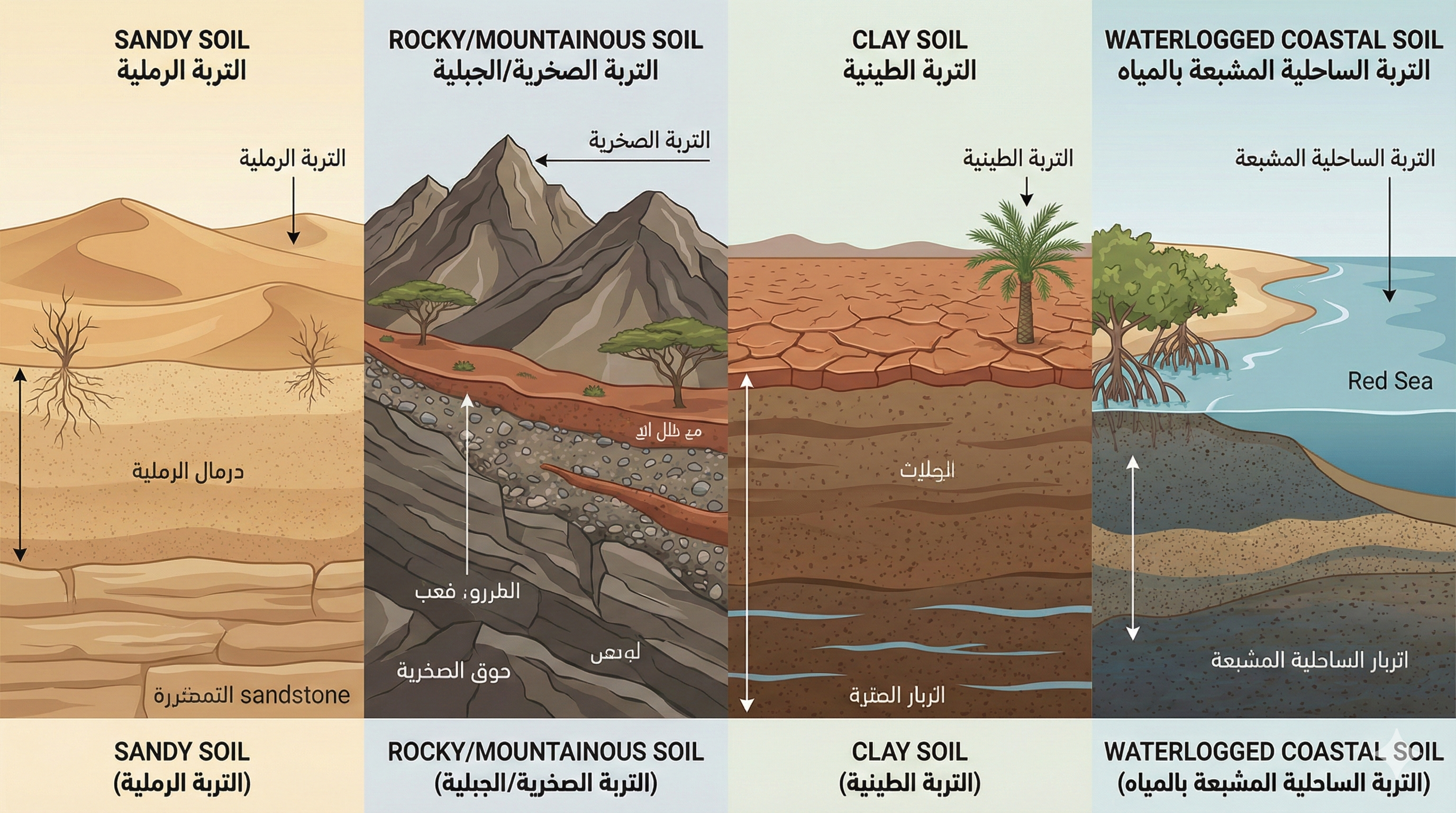
Chapter One: Soil Types in Saudi Arabia and Their Characteristics
Soil varies greatly in Saudi Arabia due to different terrains from coast to mountains to desert. Understanding your land's soil type is the first step to avoiding costly surprises.
Sandy Soil
Most common in the Kingdom, especially in desert and coastal areas. Consists of relatively large particles and is characterized by easy excavation. However, its main problem is that it doesn't retain water and excavation sides may collapse if not supported. Load-bearing capacity ranges from 1 to 4 kg/cm² depending on compaction.
Clay Soil
Found in agricultural areas and wetlands. Consists of very fine particles and is characterized by high cohesion. Its major problem is shrinking when dry and expanding when wet, causing foundation movement and building cracks. Bearing capacity ranges from 0.5 to 3 kg/cm².
Rocky Soil
Found in mountainous areas like Taif, Abha, Jazan, and parts of Riyadh. It's the best soil type for construction in terms of bearing capacity reaching 30-40 kg/cm². However, the problem is the difficulty and high cost of excavation.
Gravel Soil
A mixture of gravel and sand, found in valley beds and plains. Considered good soil for construction with bearing capacity ranging from 4 to 8 kg/cm². Relatively easy to excavate and provides good water drainage.
Saline Soil and Sabkha
Found in coastal areas especially on the Arabian Gulf. Contains high salt content that causes concrete and steel corrosion. Requires special treatment and use of salt-resistant cement.
Organic and Marshy Soil
Rare in Saudi Arabia but exists in some old agricultural areas. Not suitable for direct construction and needs removal and replacement with suitable soil.
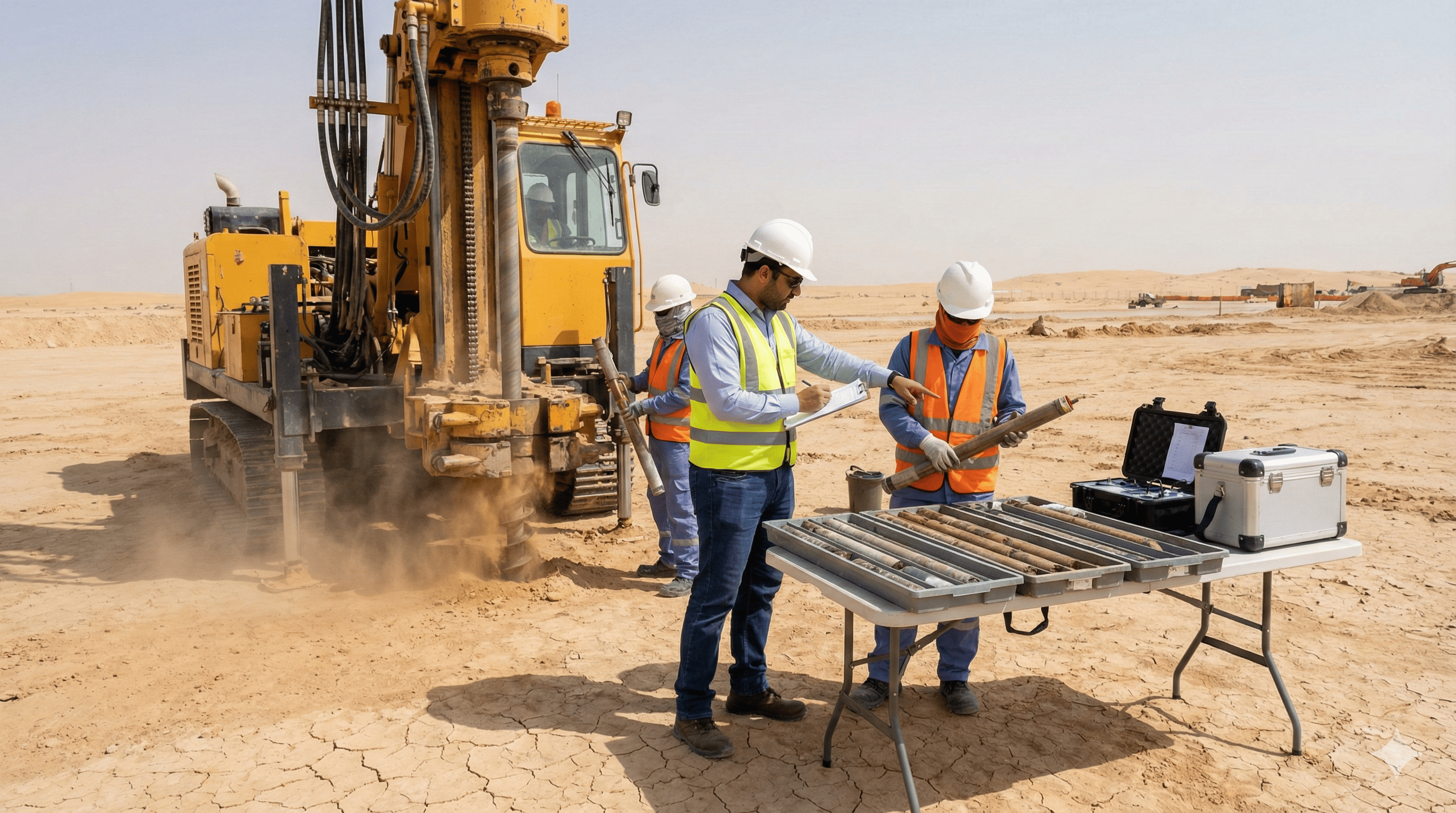
Chapter Two: Soil Testing (Boreholes) - The Mandatory Step
Soil testing, known as boreholes (Gesat), has become mandatory in Saudi Arabia for obtaining building permits according to the Saudi Building Code. But even if it weren't mandatory, it's a smart investment that protects you from losses that could reach millions of riyals.
What Is Soil Testing?
It's the process of taking soil samples at different depths and analyzing them in the laboratory to determine their physical, chemical, and mechanical properties. This is done by drilling small wells called boreholes at multiple points on the land.
What Does the Soil Test Report Reveal?
The report reveals several vital information: soil type and layers, soil load-bearing capacity, appropriate foundation depth, groundwater presence and level, salt and sulfate percentages, and probability of settlement or shrinkage.
How Many Boreholes Are Required?
Depends on land area and project type. For small residential projects, usually 4 boreholes at land corners with one in the middle is sufficient. For large buildings and towers, the number increases according to structural engineer recommendations.
What Depth Is Required?
For regular residential projects of two to three floors, a depth of 10 to 15 meters is sufficient. For towers and multi-story buildings, depth may reach 30 meters or more.
How Much Does Soil Testing Cost?
Cost varies based on number of boreholes, depth, and type of analyses required. For small residential projects, cost ranges from 2,000 to 5,000 SAR. For a package of 4 boreholes at medium depth, cost ranges from 6,000 to 12,000 SAR. For large projects, cost may reach tens of thousands.
How Long Does Soil Testing Take?
Field work usually takes one to two days depending on number of boreholes. Laboratory analysis and report preparation takes 3 to 7 days. In total, expect one to three weeks for the final report.
Who Performs Soil Testing?
Testing must be done by a government-accredited laboratory. The engineering office supervising your project can suggest reliable laboratories. Ensure the report is certified as the municipality will require it for permit requirements.
Chapter Three: Excavation Equipment - Choosing the Right Machine
Choosing the right equipment saves time and money and ensures work safety. Equipment varies based on soil type, required excavation depth, and site area.
Excavator (Hydraulic Digger)
The primary equipment for excavation in most projects. Comes in different sizes: small under 6 tons for tight spaces, medium 6 to 10 tons for medium projects, and large 10 to 45 tons for massive projects. Daily rental price starts from 700 SAR and reaches 1,500 SAR depending on size.
Hydraulic Hammer (Rock Breaker)
Attachment mounted on excavator for breaking rocks and hard surfaces. Essential for rocky and mountainous terrain. Adds about 200 to 400 SAR extra to daily rental cost.
Loader (Shovel)
Used for moving large quantities of excavated soil quickly and efficiently. Suitable for large projects requiring massive volume transport.
JCB (Backhoe Loader)
Multi-purpose equipment with rear digging arm and front bucket. Suitable for tight sites requiring excavation and transport in the same place.
Bobcat (Skid Steer)
For very tight spaces that large excavators can't reach. Suitable for small excavation and leveling work.

Chapter Four: Rocky and Mountainous Terrain Scenario
If you bought land in a mountainous area like Taif, Abha, or some rocky areas of Riyadh, you're facing a completely different challenge from regular land.
How Do You Know Your Land Is Rocky?
Signs are clear: difficulty inserting a metal rod into the ground, rocks appearing on or near the surface, neighboring lands having the same problem. But the sure way is soil testing which will determine exactly the rock layer depth and type.
What Equipment Is Required?
For rocky terrain, you'll need an excavator with a hydraulic breaker (rock hammer). The breaker works with powerful repeated strikes to break up rocks. Some very hard rocks may require blasting with special permits, but this is rare in residential projects.
How Long Does Excavation Take?
Excavation in rocky terrain is much slower than regular soil. What can be completed in one day in regular soil may take 3 to 5 days in rock. Excavator productivity drops significantly.
How Much Does Rocky Terrain Excavation Cost?
Cost is much higher than regular soil. For regular excavation at 80cm depth in sandy soil, cost may be 4,000 to 5,000 SAR. Same depth in rocky terrain may cost 10,000 to 15,000 SAR or more. Reason is longer time, equipment wear, and need for rock breaker.
Can Cost Be Reduced?
Some tips to reduce cost: design the building to match land topography instead of fully leveling it, use extracted rock pieces for other works like retaining walls, and negotiate per cubic meter price instead of daily rate.
Rocky Terrain Advantages
Despite excavation difficulty, rocky terrain has advantages: very strong foundations, no fear of future building settlement, usually no groundwater problems, and no need for deep foundations or special soil treatments.
Chapter Five: Groundwater Scenario
One of the most frustrating problems during excavation: you start digging normally then suddenly water appears from underground and fills the excavation. This is common in coastal areas and some areas of Riyadh and Al-Ahsa.
When Does Groundwater Appear?
It appears when excavation reaches groundwater level. In coastal areas like Jeddah and Dammam, the level may be very close to the surface at one meter or less. In inland areas, it's usually deeper.
How Do You Know Beforehand?
Soil test report will tell you exactly about groundwater presence and at what depth. This is one of the most important reasons not to skip soil testing. You can also ask neighbors who built before you.
What Are the Dewatering Methods?
There are several methods depending on water quantity and depth:
First method is surface dewatering by making a collection sump in an excavation corner and pumping water with submersible pumps. This is the simplest and cheapest method for small quantities.
Second method is wellpoint system where small wells are drilled around the excavation site connected to a central pump. This method is effective for lowering water level before starting excavation.
Third method is deep wells for large projects or when water level is very deep.
How Much Does Dewatering Cost?
Cost depends on water volume and work duration. For small projects, submersible pump rental starts from 200 SAR daily. Wellpoint system may cost thousands of riyals for installation plus daily operating cost. Generally, expect adding 20% to 50% to regular excavation cost.
What After Dewatering?
After completing foundations, excellent waterproofing must be done to protect the building from future moisture. Using water-resistant concrete and rust-treated steel is essential in these cases.

Chapter Six: Clay Soil Scenario
Clay soil may seem easy to excavate, but it hides serious problems that need attention.
What's the Problem with Clay Soil?
The main problem is shrinkage and expansion. When clay soil dries it shrinks and cracks, and when exposed to water it expands. This continuous movement causes pressure on foundations and may lead to building cracks.
How Do You Excavate in Clay Soil?
Excavating in dry clay soil is relatively easy. The problem is when it's wet where it sticks to equipment and makes work difficult. Excavating in dry season is preferable if possible.
What Are the Engineering Solutions?
There are several solutions: removing clay soil and replacing with sandy or gravel soil (soil replacement), making deeper foundations beyond the clay layer, using pile foundations, or making an insulating layer around foundations.
How Much Does Treatment Cost?
Soil replacement costs from 50 to 100 SAR per cubic meter including removal, supply, and compaction. Piles are much more expensive starting from 500 SAR per linear meter.
Chapter Seven: Coastal Land Scenario
Building near the sea has special challenges combining groundwater problems, salinity, and loose soil.
What Problems Are Expected?
Groundwater level very close to surface, sandy soil saturated with water and unstable, high salt content causing concrete and steel corrosion, and tide effect on water level.
How Do You Handle It?
Using salt and sulfate resistant cement, increasing concrete cover thickness to protect steel, double waterproofing, and permanent drainage system around the building. You may need pile foundations to reach a solid layer.
How Much Does Cost Increase?
Expect foundation cost increase by 30% to 100% compared to regular land. This includes special treatments, resistant materials, and dewatering system.
Chapter Eight: Excavation Cost Table 2025
These are approximate prices from the Saudi market and may vary by region and season:
Soil Testing Cost
Simple test with two boreholes: 2,000 to 3,000 SAR. Standard test with four boreholes: 4,000 to 6,000 SAR. Comprehensive test for large projects: 10,000 to 30,000 SAR.
Equipment Daily Rental
Small excavator: 600 to 800 SAR. Medium excavator: 800 to 1,200 SAR. Large excavator: 1,200 to 1,500 SAR. Excavator with rock breaker: additional 200 to 400 SAR. Loader: 500 to 700 SAR. Dump truck for soil transport: 300 to 500 SAR per trip.
Excavation Cost by Soil Type
Regular sandy soil at 80cm depth: 4,000 to 6,000 SAR for medium villa. Rocky soil: 10,000 to 20,000 SAR. Soil with groundwater: 8,000 to 15,000 SAR including dewatering.
Treatment Costs
Soil replacement: 50 to 100 SAR per cubic meter. Dewatering: 500 to 2,000 SAR daily depending on system. Piles: 500 to 1,500 SAR per linear meter.
Chapter Nine: Golden Tips Before Starting
Don't Skip Soil Testing
Its cost is minimal compared to disasters it may save you from. The report gives you a clear picture of what awaits and helps the engineer design appropriate foundations.
Consult Neighbors
Before buying or excavating, ask those who built in the same area. Did they face groundwater? Is the land rocky? Their experience saves you a lot.
Choose the Right Contractor
Not every excavation contractor can handle difficult terrain. Ask about their experience with your specific soil type and request references from similar projects.
Plan for Transport
Excavated soil needs transport. In some cases it can be used for later backfill, but sometimes you need to dispose of it. Calculate transport cost within budget.
Excavation Timing Matters
Avoid excavating in rainy season especially for clay soil. Summer is better for land that may contain seasonal groundwater.
Keep Budget Margin
Excavation surprises are common. Keep an extra 20% in budget for any emergencies that may appear.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Soil Testing Mandatory for Villa Construction?
Yes, it has become mandatory according to Saudi Building Code and required for building permit issuance. Even if not mandatory in your area, we strongly recommend it.
How Long Does Excavating 400 Square Meter Land Take?
Depends on soil type. For regular soil: one to two days. For rocky soil: 5 to 10 days. Groundwater presence adds 2 to 3 days.
What If Unexpected Rocks Appear During Excavation?
This happens sometimes even with soil testing. Solution is renting a rock breaker. Cost and time will increase, but it's a solvable problem.
Can I Build on Land with Groundwater?
Yes, millions of buildings worldwide are built over groundwater. What matters is correct design, good waterproofing, and appropriate drainage system.
Who Determines Appropriate Foundation Type?
The structural engineer based on soil test report, building type, and number of floors. Don't leave this decision to the contractor.
Can I Use Excavated Soil for Later Backfill?
If excavated soil is suitable and clean, it can be used. But organic soil or soil mixed with waste is not suitable for backfill. The engineer determines this.
Conclusion: Excavation Is Not Just a Hole in the Ground
Excavation is the foundation of everything that follows. Understanding your soil type, doing necessary tests, choosing correct equipment, and preparing for potential problems saves you much time, money, and worry.
Don't rush this phase and don't skimp on it. A strong foundation starts from deep knowledge of the land you'll build on. Invest in soil testing, choose an experienced contractor, keep a budget for emergencies, and you'll find that this phase that many fear will pass smoothly.
